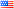
Great Egret ( Ardea alba ( ex Casmerodius albus )
- Sent by Rodrigo Girardi Santiago - 17/03/2007
- 32.871 visits
- 660 downloads
- 0 comments
91cm. The neck and the legs are thin and long. All white, but with iris, beak and legs yellow.
Distribution:
Throughout the world.
Habitat:
Lakes, rivers, ponds, reservoirs, swamps, mangroves, estuaries and even polluted rivers.
Diet:
Eats fishes, amphibians, insects. The author witnessed an egret catching and eating a mouse in a riverbank in Campinas-SP.
Reproduction:
Breeding takes place generally in the end of the dry season, when the food supply is more abundant for this species. During this period the adults have the egrets that are long feathers used in the courtship. The breeding couples gather in nesting sites that may have hundreds of individuals, sometimes mixing with other species.
Natural history:
It is the commonest species of egret in the country and also the toughest, thriving even in the polluted water of the Tietŕ river in the capital city of SŃo Paulo, feeding on carrion and waste. It may be migratory. In the past it was intensively hunted because of the egrets. Very smart, learns to use fish food (such as bread) as bait. Also begs fisherman for small fish.


 Rodrigo Girardi Santiago
Rodrigo Girardi Santiago